Over 84,000 Roundcube webmail installations are weak to CVE-2025-49113, a essential distant code execution (RCE) flaw with a public exploit.
The flaw, which impacts Roundcube variations 1.1.0 by means of 1.6.10, spanning over a decade, was patched on June 1, 2025following its discovery and reporting by safety researcher Kirill Firsov.
The bug stems from unsanitized $_GET(‘_from’) enter, enabling PHP object deserialization and session corruption when session keys start with an exclamation mark.
Shortly after the patch was launched, hackers reverse-engineered it to develop a working exploit, which they bought on underground boards.
Although the exploitation of CVE-2025-49113 requires authentication, attackers declare that legitimate credentials may be obtained by way of CSRF, log scraping, or brute-forced.
Firsov shared technical particulars in regards to the flaw on his weblog to assist defend towards lively exploitation makes an attempt which might be very more likely to happen.
Large publicity
Roundcube is extensively utilized in shared internet hosting (GoDaddy, Hostinger, OVH) and authorities, training, and tech sectors, with over 1,200,000 situations seen on-line.
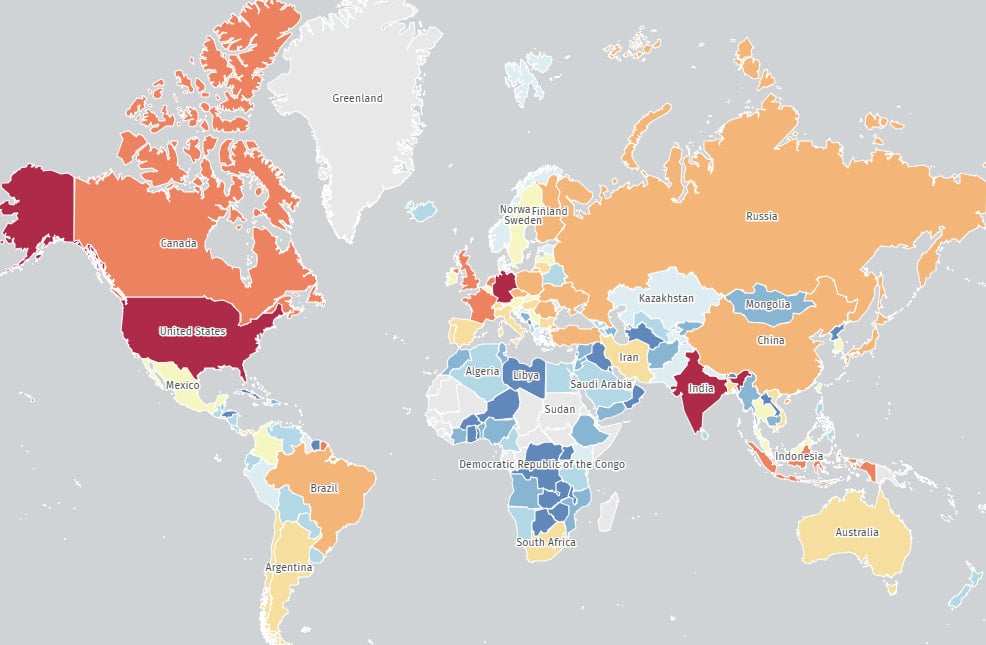
Risk monitoring platform The Shadowserver Basis reviews that its web scans return 84,925 Roundcube situations weak to CVE-2025-49113 as of June 8, 2025.
Most of those situations are in the USA (19,500), India (15,500), Germany (13,600), France (3,600), Canada (3,500), and the UK (2,400).
Supply: The Shadowserver Basis
Contemplating the excessive danger of exploitation and the potential for knowledge theft, the publicity of these situations is a big cybersecurity danger.
System directors are advisable to replace to model 1.6.11 and 1.5.10, which handle CVE-2025-49113, as quickly as attainable.
It’s unclear if the flaw is being leveraged in precise assaults and at what scale, however quick motion is suggested nonetheless.
If upgrading is unattainable, it’s endorsed to limit entry to webmail, flip off file uploads, add CSRF safety, block dangerous PHP features, and monitor for exploit indicators.
Patching used to imply complicated scripts, lengthy hours, and countless hearth drills. Not anymore.
On this new information, Tines breaks down how fashionable IT orgs are leveling up with automation. Patch quicker, cut back overhead, and concentrate on strategic work — no complicated scripts required.


