Samsung Electronics has printed a paper with Sungkyunkwan College (SKKU) on an electrochemical water therapy expertise able to energy restoration in Joule, a world-renowned journal within the subject of vitality analysis.
Titled “Divalent and Halide Twin-Ion Storage of a Redox-Lively Symmetric Cell for an Environment friendly Wastewater-Vitality Nexus,” the paper presents a brand new paradigm for concurrently implementing water therapy and vitality storage whereas addressing the excessive energy consumption and value problems with current electrochemical water therapy applied sciences. Particularly, the analysis demonstrates that vitality effectivity could be enhanced by supplying energy generated from the electrode regeneration course of to exterior units — displaying potential for broad utility in numerous industries in addition to every day life.
The research was collectively performed by the Life Resolution Crew at Samsung Analysis of Samsung Electronics and the analysis group led by chemical engineering professor HoSeok Park at SKKU. Samsung participated in your entire course of — from ideation to experiment design, implementation and validation — considerably contributing to proving the potential of the distinctive electrochemical water therapy expertise.

A global tutorial journal that covers cutting-edge vitality applied sciences, Joule was established by Cell Press in 2017 and is very influential throughout bodily chemistry, vitality and fuels, supplies science and different scientific fields. The paper’s publication marks a milestone for Samsung Analysis and SKKU.
Overcoming the Limits of Electrochemical Water Therapy
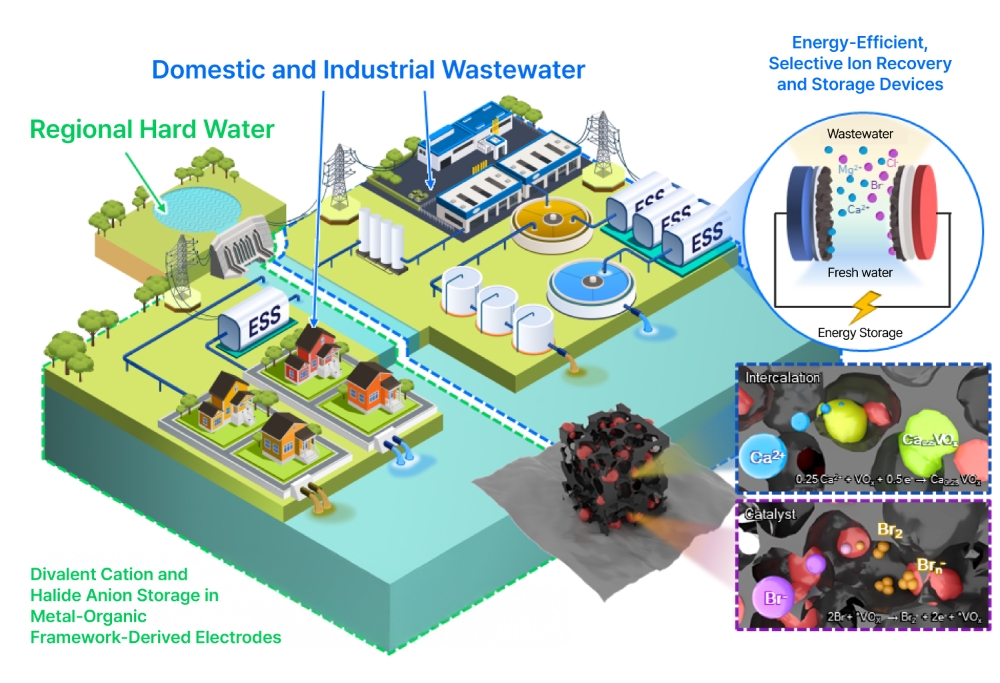
Electrochemical water therapy applied sciences are based mostly on capacitive deionization (CDI), whereby voltage is utilized to an electrode, inflicting ions in water to adsorb onto the electrode by electrostatic forces. This removes the ions from the water, purifying it. The tactic is particularly efficient in opposition to hardness ions (Ca²⁺, Mg²⁺) that scale back the detergency of cleansing brokers and result in scale buildup.
Not like membrane-based water therapy applied sciences, which make use of skinny limitations to selectively permit or block the passage of liquid or fuel microparticles, electrochemical applied sciences use no bodily filters. Because of this, upkeep and restore are simpler, making these applied sciences an energetic space of analysis.
Regardless of their benefits, electrochemical water therapy applied sciences nonetheless face sure challenges. Further energy is consumed within the electrode regeneration course of, and the required use of ion trade membranes — which selectively permit ions with a selected electrical cost to move whereas stopping their re-adsorption — stays an impediment to commercialization as a consequence of elevated prices.
To beat these limitations, the Samsung Analysis-SKKU group developed a next-generation electrochemical water therapy expertise that may be utilized with out ion trade membranes. The expertise gives low module composition prices, allows the removing of enormous volumes of hardness ions and may provide the ability generated within the electrode regeneration course of to exterior units — paving the best way for its potential as a multifunctional water therapy resolution.
A New Strategy to Ion Storage With a Subsequent-Technology Electrode
The analysis group used a metallic oxide-based nanostructure — a departure from typical electrode supplies — to create their electrode. In comparison with typical designs, this newly developed electrode demonstrated a 200% enhance in ion storage capability and a 20% enchancment in storage fee.
Typical electrode supplies take away ions by electrostatic forces, requiring costly ion trade membranes to stop re-adsorption throughout electrode regeneration. The brand new electrode, nevertheless, allows ions to be saved and spontaneously desorbed by direct electron trade, eliminating the necessity for an ion trade membrane.
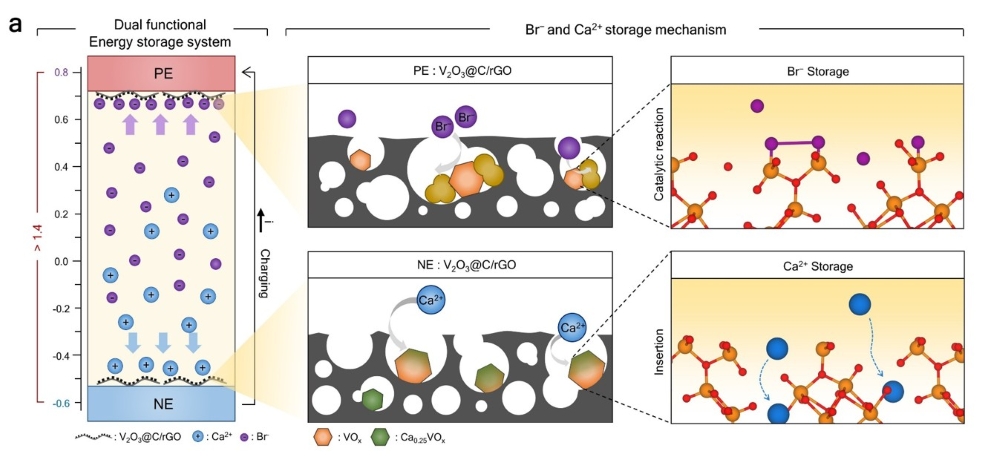
The Potential To Evolve Right into a Multifunctional Vitality System
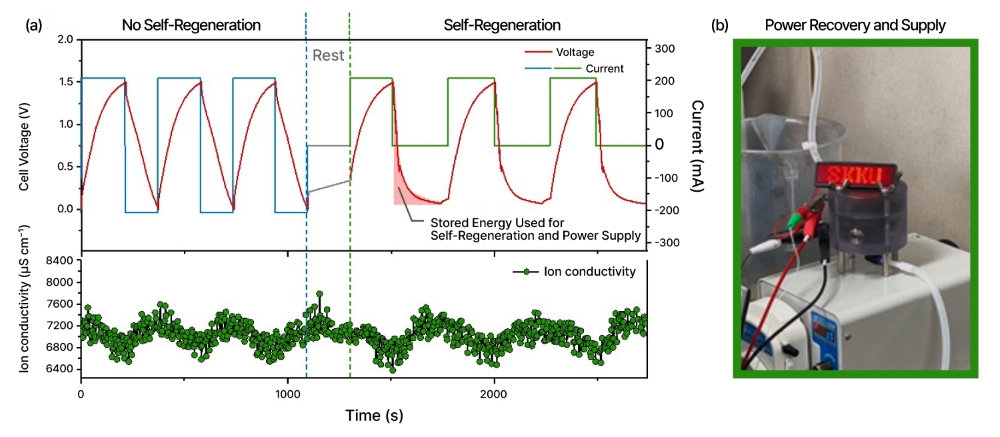
For repeated operation, current electrochemical water therapy applied sciences additionally require electrode regeneration by the availability of extra energy. Throughout this course of, sudden ion leakage could cause an overcurrent and reverse the polarity of the electrodes, making it inconceivable to make the most of the saved vitality.
The following-generation water therapy electrode developed by Samsung Analysis and SKKU is free from this problem, as spontaneous electrode regeneration could be achieved with out the availability of extra energy. Moreover, it will possibly recuperate saved vitality and provide energy to close by units. The group additionally discovered that the ability required to function an electrochemical water therapy module utilizing this expertise was 76Wh/kg — about half that of current applied sciences.
Future Enlargement to Dwelling Home equipment and Environmental Options
With its progressive new electrode, the electrochemical water therapy module developed by Samsung Analysis and SKKU has the potential to function a multifunctional unit that may deal with water whereas supplying backup energy for numerous residence home equipment that use water, similar to dishwashers, washing machines and water purifiers. It’s anticipated to play a key position as an progressive expertise of the longer term.
Constructing on this research, Samsung plans to strengthen industry-academia collaboration and broaden its analysis efforts to safe the core applied sciences that can form the way forward for the surroundings and vitality sectors. By these initiatives, the corporate goals to speed up the event of progressive options for a extra sustainable tomorrow.

